

The first hypothesis regarding faster-than-light particles is sometimes attributed to German physicist Arnold Sommerfeld in 1904, who named them "meta-particles". In his paper he also introduced fields with imaginary mass (now also referred to as tachyons) in an attempt to understand the microphysical origin such particles might have. Feinberg studied the kinematics of such particles according to special relativity. He had been inspired by the science-fiction story "Beep" by James Blish. The term tachyon was coined by Gerald Feinberg in a 1967 paper titled "Possibility of faster-than-light particles". 3.3 Fields with non-canonical kinetic term.The complementary particle types are called luxons (which always move at the speed of light) and bradyons (which always move slower than light) both of these particle types are known to exist. The term comes from the Greek: ταχύ, tachy, meaning swift. Such fields play a significant role in modern physics. Nevertheless, in modern physics the term tachyon often refers to imaginary mass fields rather than to faster-than-light particles. However, it was soon realized that Feinberg's model did not in fact allow for superluminal (faster-than-light) particles or signals and that tachyonic fields merely give rise to instabilities, not causality violations. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a quantum field with imaginary mass. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow down to the speed of light. According to the theory of relativity this would violate causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. If such particles did exist they could be used to send signals faster than light.
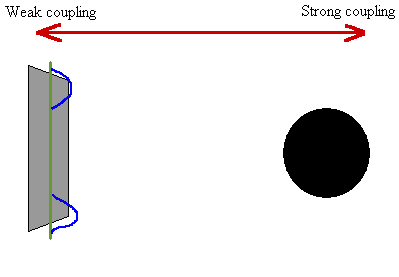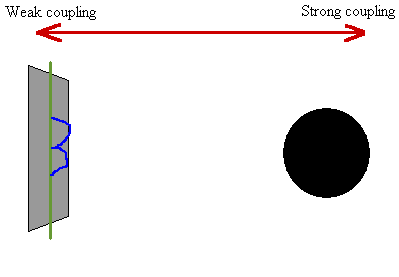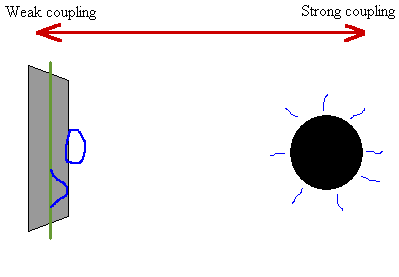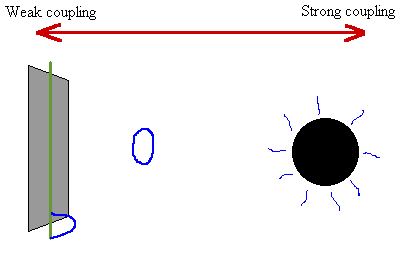
Physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics. Because the tachyon arrives before the light, the observer sees nothing until the sphere has already passed, after which (from the observer's perspective) the image appears to split into two-one of the arriving sphere (to the right) and one of the departing sphere (to the left).Ī tachyon ( / ˈ t æ k i ɒ n/) or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. This double-image effect is most prominent for an observer located directly in the path of a superluminal object (in this example it is a sphere, shown in transparent grey). After a tachyon has passed nearby, an observer would be able to see two images of it, appearing and departing in opposite directions. Because a tachyon would always travel faster than light, it would not be possible to see it approaching.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
